Demos/Code/Data
Sketch-based Retrieval in Databases with Millions of Images (Sarthak Parui and Anurag Mittal, ECCV 2014)
Some Results:
Contour-based Object Detection in an Image using a Single Sketch (S.D. Bhattacharya and Anurag Mittal, CVIU 2015; Sai Prasad, Arpit Jain and Anurag Mittal, ECCV 2008)
A single contour-based object model is used to match all the instances of the model in the images. The model is automatically segmented into parts using geometric analysis. Each part is matched under affine deformations of the part and the parts can deform with respect to each other at the junction points. Note that in the following images, a single apple model is used for the different apple detections and a single duck model is used for the different duck detections.
Feature Detection, Description and Matching (R. Gupta and Mittal, ICCV 2007, ECCV 2008, CVPR 2010)
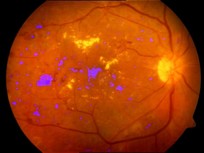
Please follow this link for a short description and code.Diabetic Retinopathy (Sai Prasad, Arpit Jain and Anurag Mittal, ECCV 2008)
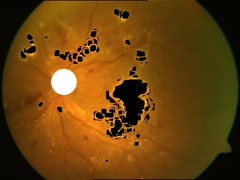
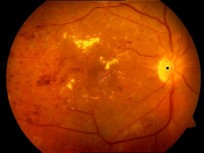
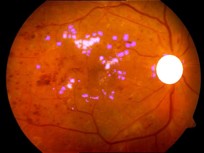
Detection of Optic Disk (the circular structure from where the blood vessels originate), Exudates (yellow patches) and Microaneurisms (Red Blood clots) for early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus images.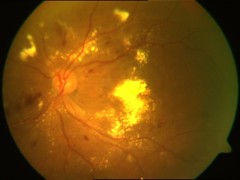
Background Subtraction in Dynamic Backgrounds (Mittal, Monnet and Paragios, CVIU 2009; Mittal and Paragios, CVPR 2004; Mittal, Paragios and V. Ramesh, ICCV 2003)
Detection result from CVIU 2009 and ICCV 2003 papers that use a dynamical model in a PCA subspace Zip File . An interesting generic method that might be computationally expensive for some applications.Multiple Camera Detection and Tracking (A. Gupta and Mittal, ICCV 2007; Mittal and Davis, IJCV 2003),
Tracking result from ICCV 2007 view1 view2 view3 view4

Multiple Camera Human Pose Estimation (A. Gupta and Mittal, PAMI 2008; Mittal, Zhao and Davis, 2003)
Pose results from PAMI 2008 view1 view2


3D Morphing (Mahesh Ramasubramanium and Anurag Mittal, ICMCS 1999)